Bridge Crane vs. Gantry Crane: Key Differences Explained
Meta Description: Discover the differences between bridge cranes and gantry cranes. Learn their structures, applications, and which one suits your industrial needs.

Introduction
Bridge cranes and gantry cranes are two widely used material-handling solutions in industrial settings. While they share similarities in lifting heavy loads, their designs, mobility, and applications differ significantly. This article breaks down their key distinctions to help you choose the right equipment for your operations.
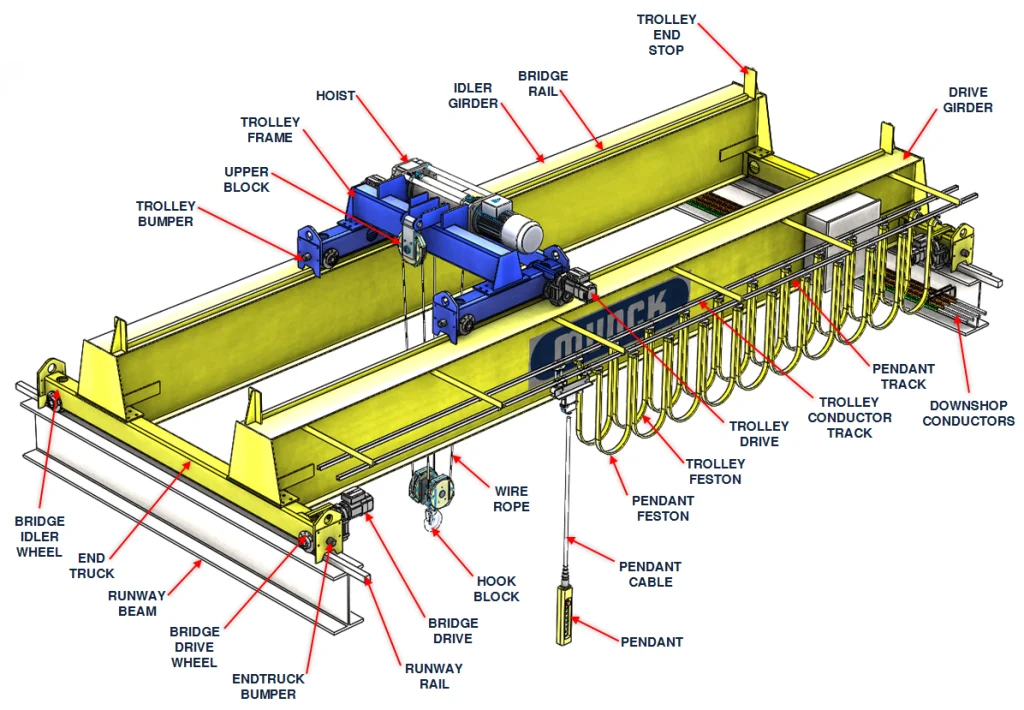
1. Structural Design
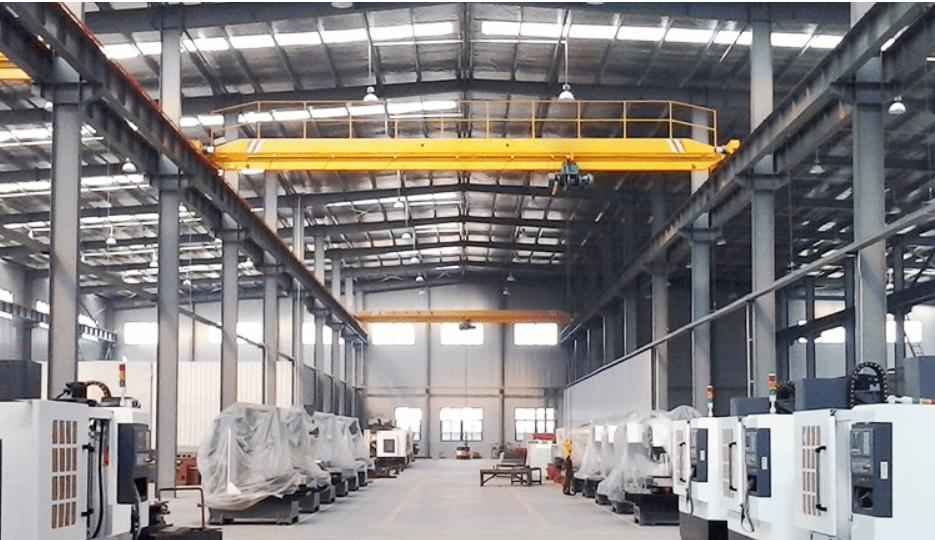
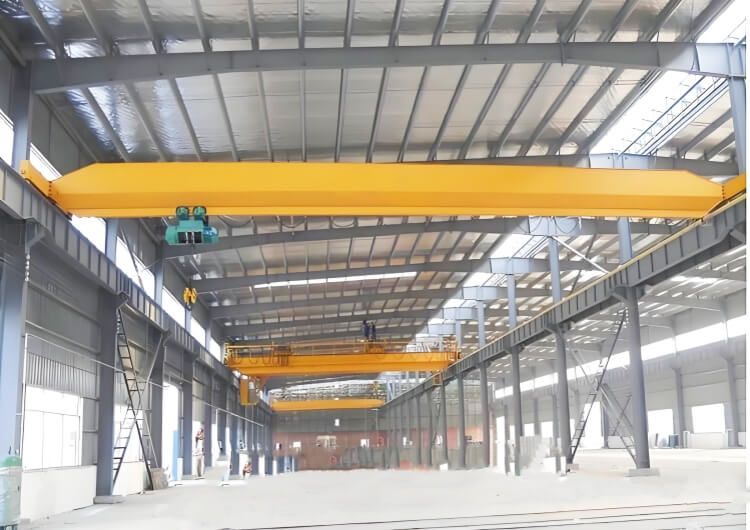
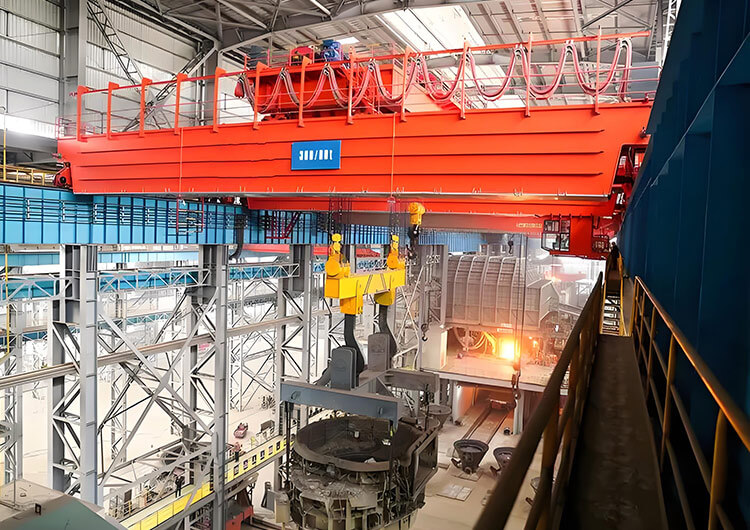
Bridge Crane:
Features a fixed overhead runway system installed on a building’s support structure.
Consists of a horizontal bridge (girder) that moves along elevated rails.
Ideal for indoor use in factories, warehouses, or workshops with existing support structures.

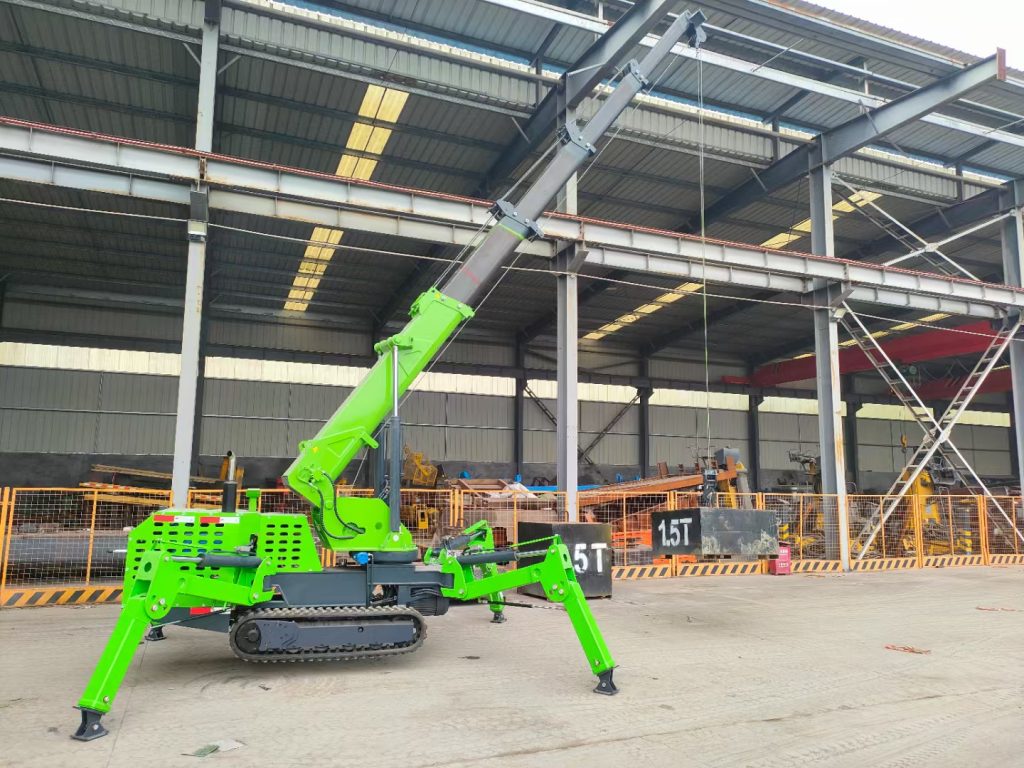
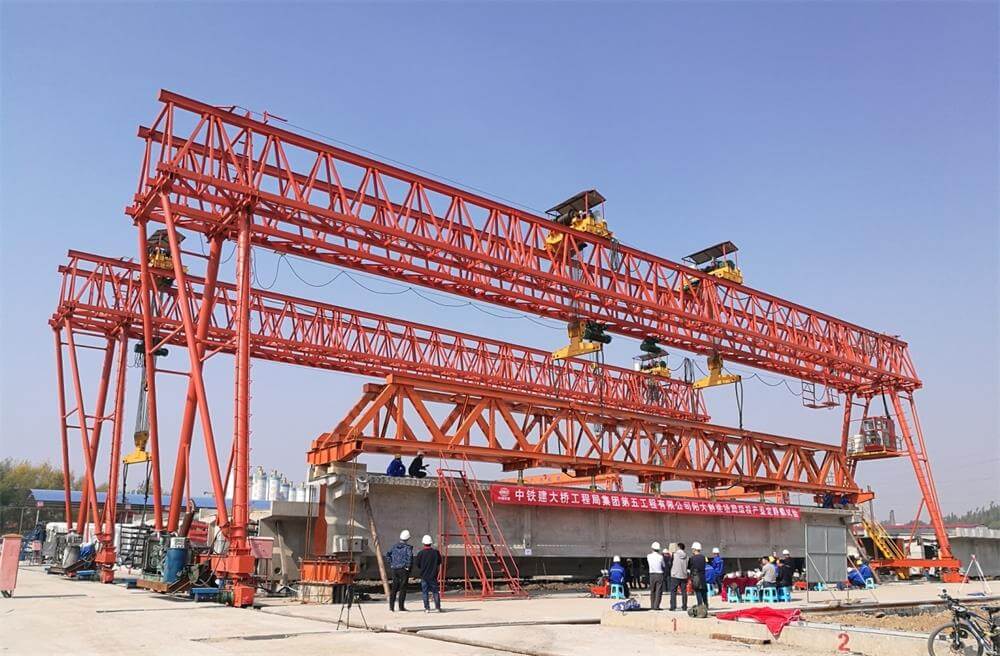
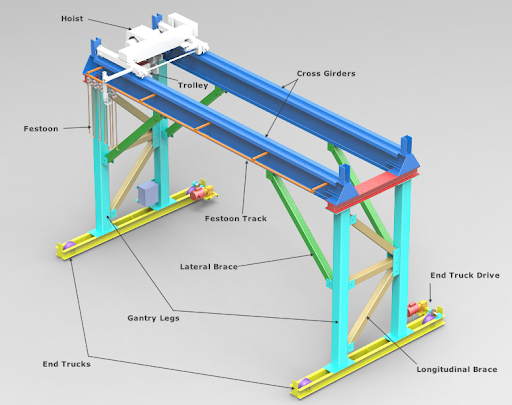
Gantry Crane:
A portable system with a freestanding framework supported by legs on the ground.
The bridge moves on wheels or rails embedded in the floor, requiring no building support.
Commonly used outdoors (e.g., shipping yards, construction sites) or in facilities with limited overhead space.
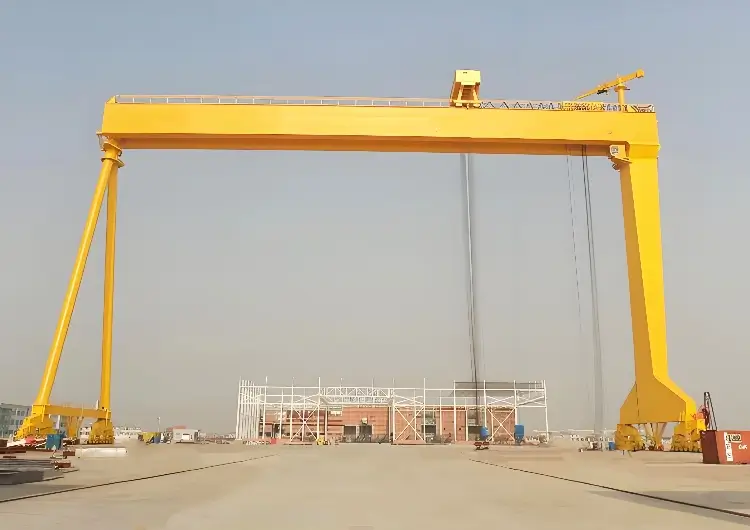

2. Mobility and Flexibility
Bridge Crane:
Limited to the length of the installed runway system.
Best for repetitive tasks within a confined area.
Gantry Crane:
Highly mobile and adjustable; can be relocated as needed.
Suitable for projects requiring movement across large or open areas.
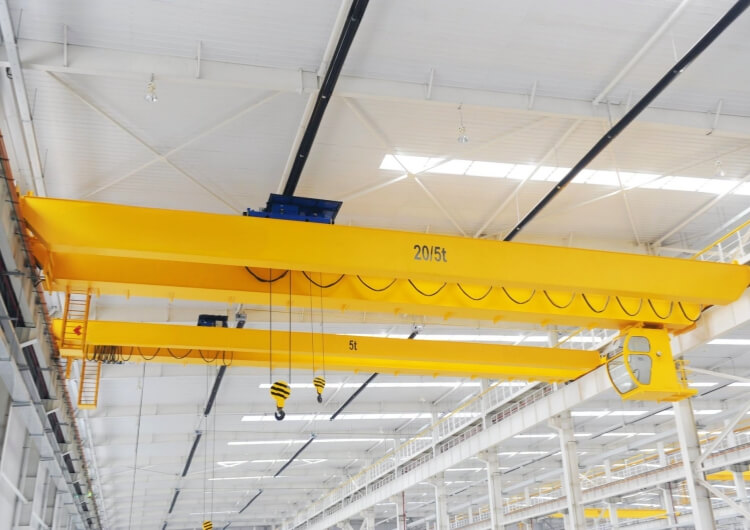
3. Load Capacity
Bridge Crane:
Typically handles heavier loads (up to 500 tons) due to robust structural support.
Used in steel mills, heavy machinery plants, and automotive manufacturing.
Gantry Crane:
Lower load capacity (usually up to 20–50 tons) but sufficient for smaller-scale operations.
Ideal for loading/unloading cargo, construction materials, or shipping containers.
4. Cost and Installation
Bridge Crane:
Higher installation costs due to fixed infrastructure requirements.
Long term cost-effective for high-volume, indoor operations.
Gantry Crane:
Lower upfront costs and easier setup with minimal infrastructure.
Portable design reduces long-term investment in permanent structures.
5. Applications
Bridge Crane:
Manufacturing assembly lines.
Heavy duty material handling in enclosed facilities.
Gantry Crane:
Outdoor construction sites.
Ports, rail yards, and logistics hubs.
Conclusion
Bridge cranes excel in indoor environments requiring heavy lifting and precision, while gantry cranes offer versatility for outdoor or temporary projects. Your choice depends on load requirements, workspace constraints, and budget. Evaluate your operational needs to select the most efficient and cost effective solution.
All News
Recent Posts
2025/1/25
2025/2/7
Contact Us Now
Have questions about our cranes or need help?
Reach out to our friendly team for expert support and guidance.
We are here to help you power your journey towards a greener future !
Tel: +8615738677559
E-mail: [email protected]
Whatsapp: +8615738677559
Address: Crane Industry Park, Xinxiang City Henan Provice





